Milankovitch Cycles and Climate: Part I – Axial Tilt and Precession
The theory of Milankovitch cycles is named after Serbian astronomer and geophysicist, Milutin Milanković, who in the 1920s postulated three cyclical movement patterns related to Earth’s orbit and rotation and their resultant effects on the Earth’s climate. These cycles include axial tilt (obliquity), elliptical eccentricity, and axial precession. In aggregate, these cycles contribute to profound long term changes in earth’s climate via orbital forcing.
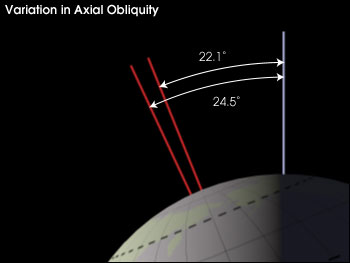
Axial Obliquity:
The Earth’s rotational axis is always tilted slightly; currently, its axis is about 23.4 degrees from the vertical. Alternatively, you could say that its equatorial plane is tilted about 23.4 degrees relative to its orbital plane. This tilt is responsible for Earth’s seasons. During the Northern Hemisphere (NH) summer, Earth is further away from the Sun than it is during the NH winter due to its slightly elliptical orbit, yet it receives more sunlight because it’s tilted towards the Sun. During this same time period, the Southern Hemisphere (SH) is tilted away from the Sun, which is why NH summer coincides with SH Winter and vice versa. Contrastingly, during the NH winter, the Earth is closer to the Sun, yet receives less sunlight because it’s tilted away from it. During that same period, the SH is tilted towards the Sun, and is thus experiencing summer. (more…)